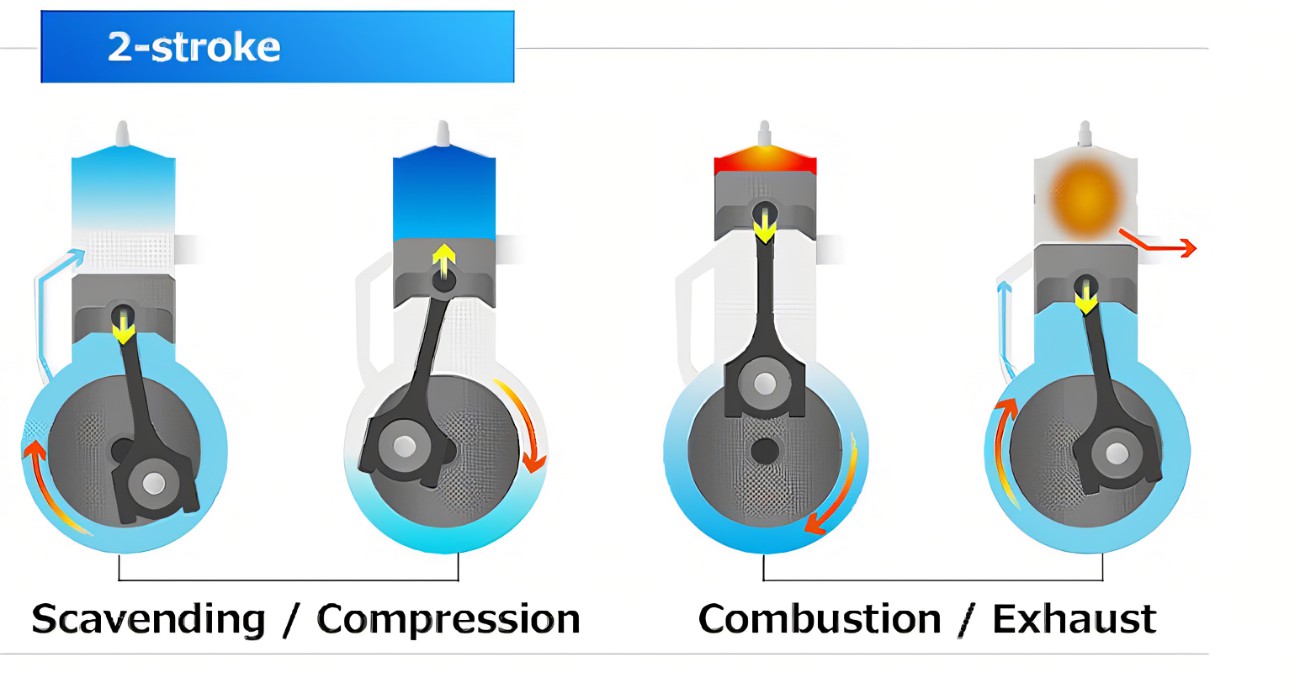
Two-Stroke Engines A two-stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle in just two strokes of the piston: intake and exhaust combined, and compression and power combined. These engines are commonly used in small applications such as chainsaws, leaf blowers, and model airplanes, where their lightweight and compact design provides a significant advantage. Two-stroke engines have a simpler design compared to four-stroke engines, with fewer moving parts, which makes them easier to maintain and repair. However, they typically consume more fuel and produce more emissions due to the nature of their combustion process. Additionally, two-stroke engines require oil to be mixed with the fuel to lubricate the engine, which can lead to increased oil consumption and environmental impact. Four-Stroke Engines A four-stroke engine, on the other hand, completes a power cycle in four strokes of the piston: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. These engines are widely used in passenger vehicles, trucks, and industrial equipment due to their better fuel efficiency and lower emissions. Four-stroke engines have a more complex design with valves that control intake and exhaust, and a separate lubrication system that eliminates the need to mix oil with fuel. This design results in better fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and longer engine life. Four-stroke engines also tend to operate more quietly and smoothly compared to two-stroke engines, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Key Differences and Applications The primary differences between two-stroke and four-stroke engines lie in their design, efficiency, and applications. Two-stroke engines are ideal for small, lightweight applications where power-to-weight ratio is crucial, and the engine's simplicity and light weight are significant advantages. In contrast, four-stroke engines are better suited for larger applications where fuel efficiency, longevity, and reduced emissions are prioritized. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the right engine type for specific needs, whether it's for a small handheld tool or a large industrial machine. Each type of engine has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right one depends on the specific requirements of the application. Empowering Future Automotive Professionals Our Department of Mechanical and Automobiles provides students with comprehensive knowledge and hands-on experience in mechanical engineering and automotive technology. With state-of-the-art facilities and expert faculty, we equip students with the skills and expertise required to excel in the automotive industry.
Two Stroke and Four Stroke Engines

Author
SCAD Poly
2025-04-12